Setting up SPI NAND on Nordic’s nRF5340 (from A to Z)
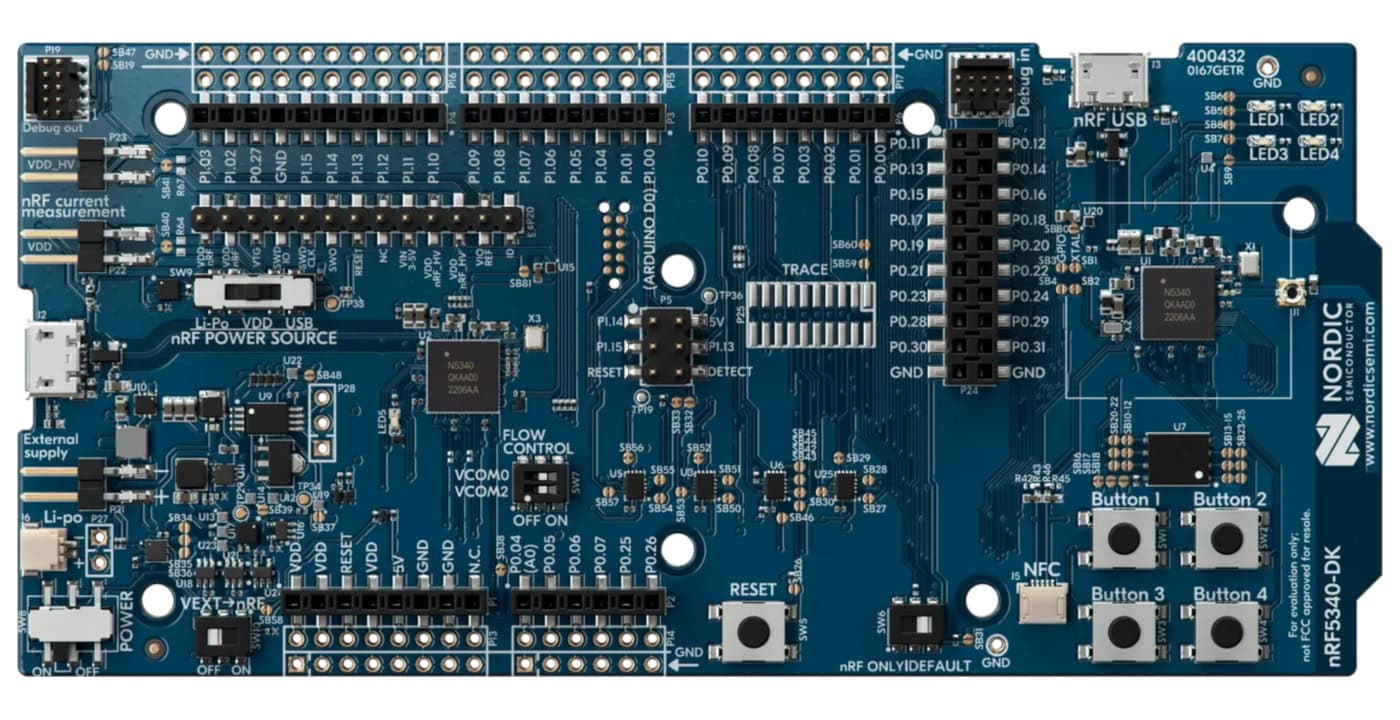
In this article, we explain how to connect, configure and access a serial NAND device connected through SPI to the Nordic Semiconductor’s nRF5340 MCU. In the process, we discuss serial flash fundamentals, write a fully functional SPI flash driver, and compare SPI and QSPI performances. For demonstration purposes, we use the nRF5340-DK development kit which